Urine Culture – Bacteriologic Exam
POWERCHART ORDER – Urine Culture
Useful For
Urinary tract infections (UTI) are a commonly encountered infectious disease. With the exception of the distal urethra, the urinary tract is traditionally considered normally sterile.
Most UTIs are due to ascension of urinary tract pathogens that colonize the vagina and intestinal tract. However, infection with some organisms such as yeast and S. aureus may occur by the descending route from the bloodstream.
UTI syndromes include asymptomatic bacteriuria, cystitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, and intrarenal abscesses.
A urine culture is used to determine the presence and significance of possible infection with bacteria and fungi in the urine. A calibrated inoculum with corresponding colony counts from a urine culture are crucial in evaluating the significance of the isolated organisms.
Method Name
Culture
Aliases
Urine Culture; Urine C&S,Urine
Specimen Type
- Clean catch, mid-stream, random – The first void is passed and the mid-stream specimen is collected. This will remove contaminating bacteria from the distal urethra.
- Indwelling catheter – Urine is collected using a syringe connected to the tubing or port between the patient and the collection bag. Do not collect directly from the collection bag.
- Straight catheter (in and out) – A catheter is inserted solely for the collection of a specimen.
- Cystoscopy – Urine is collected aseptically at time of cystoscopy, usually done in the OR or special procedures.
- Suprapubic aspirates – Urine is collected by aspiration from the bladder through the abdominal wall. With aseptic collection this should be one of the best specimen types
- Ileal conduit – Procedure performed on patients from whom the bladder is removed. A portion of the ileum is removed and used to connect the ureters to a stoma or opening in the abdominal wall. A urine collection bag is attached to the stoma. After cleansing, this specimen is collected through the stoma with a catheter.
- Nephrostomy – Collected directly from the kidney, either via a drain or surgical procedure. Nephrostomy tubes can become colonized. Collecting post nephrostomy tube change will yield a higher quality specimen.
- Anaerobic culture (order Anaerobic Culture): ONLY surgically obtained urine samples in which efforts of proper sterile technique have been implemented are acceptable for anaerobic urine culture testing. This is restricted to samples targeting direct aspiration of kidneys or suprapubic aspirates.
Specimen Required
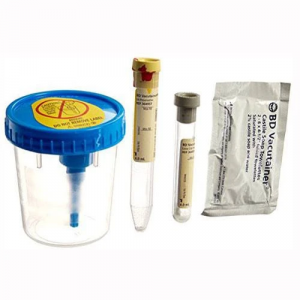
- Urine C&S Collection kit (preferred) – Gray top vacutainer tubes specifically for urine. Transport at room temperature. Should be received within 48hrs of collection for optimal results.
- Plain sterile container– Must be received as soon as possible after collection. If stored in refrigerator it will be stable for up to 24hrs after collection.
- Uricults are also acceptable. Transport at Room Temperature
- Surgically collected (suprapubic or cystoscopic) urine in a vacutainer urine transport tube (Gray Top)

Specimen Minimum Volume
1 – 2 mL of urine
Specimen Stability Information
- Specimen is stable for 48 hours in a vacutainer transport tube. Transport at room temperature.
- Refrigerated specimens are stable up to 24 hours after collection.
- *NOTE* Specimens that do not meet the above criteria will be rejected.
Rejected Due To
- Specimen received after 48 hours in a vacutainer transport tube. Transport at room temperature.
- Refrigerated specimens received later than 24 hours after collection.
Special Instructions
- Collect all specimens prior to the administration of antibiotics, as most antibiotics tend to concentrate in the urine and will affect culture results.
- For females, cleanse the vulva with cleansing prep, using a front to back motion, before collecting.
- For males, cleanse the head of the penis with cleansing prep before collecting.
- Specimens must be labeled with complete source and body site information.
- Clean voided specimens – use the clean catch midstream technique for urine collection. Collect voided urine directly into a clean wide mouth collection container.
- Do not use a urinal or bedpan for collection.
- Immediately transfer the specimen from the collection container to a BD Vacutainer transport tube using the Vacutainer needle and straw contained in the collection kit.
- Indwelling catheter specimens – avoid urine that has remained stagnant in the catheter tubing for any length of time. Do not collect urine from the catheter bag. As indwelling catheters increase the risk of urinary tract infections, specimens should not be taken from catheters that have been in place for an extended period (greater than 5 days).
- Avoid contamination during urine collection. Immediately transfer the specimen to a Vacutainer transport tube as indicated above.
- Straight catheter specimens – collection should be performed by a physician or trained practitioner. Specimens are obtained directly from the bladder. This procedure is not recommended because there is a risk of introducing microorganisms into the bladder. External surfaces should be cleansed prior to collection, as for clean voided specimens. Immediately transfer the specimen to a Vacutainer transport tube or refrigerate.
- Specimens from Ileal conduits, nephrostomy tubes or stents – collect after removal of the external device, by insertion of a catheter into the cleansed stoma. Immediately transfer the specimen to a Vacutainer transport tube or refrigerate.
- Cytoscopy specimens – collection is performed by the physician via insertion of the cystoscope. The midstream portion of the collection should be submitted for culture. Immediately transfer the specimen to a Vacutainer transport tube or transport the specimen immediately and refrigerate.
- Suprapubic aspiration – collection is performed by the physician using a needle and syringe to directly tap the bladder via suprapubic puncture. This method avoids the contamination associated with voided specimens and is the preferred method for infants and for patients for whom the interpretation of results of voided urine is difficult. Immediately transfer the specimen to a Vacutainer transport tube or transport the specimen immediately and refrigerate.
- U-bag collection – the external genital area of the infant should be cleansed before placement of the U-bag. The bag should be removed as soon as a specimen is obtained. Because of the high degree of contact of the urine specimen with the skin, U-bag collections are generally very poor specimens. Immediately transfer the specimen to a Vacutainer transport tube or transport the specimen immediately and refrigerate.
- Scant amounts (less than 1ml) of specimen may be submitted for culture in a clean sterile, leakproof containe, such as a sterile conical 15 ml centrifuge tube. However, these specimens must be maintained at refrigerator temperature and transported to the laboratory as soon as possible.
- Testing includes colony count and susceptibility testing when appropriate for the isolates recovered.
Performing Laboratory
Glens Falls Hospital Microbiology Laboratory
Day(s) and Time(s) Performed
- Day Shift
- 7 days per week
Analytical Time
1-3 days
Specimen Retention Time
48 hours
Analytical Time
1-3 days
